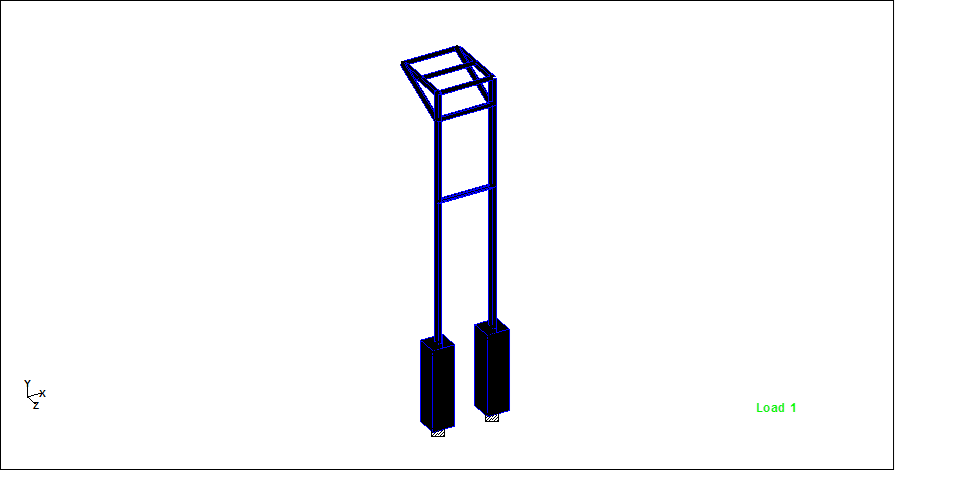
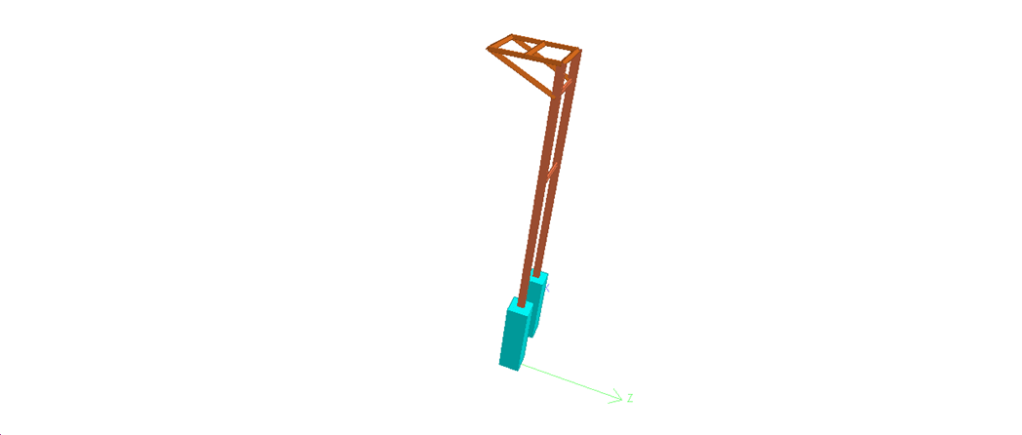
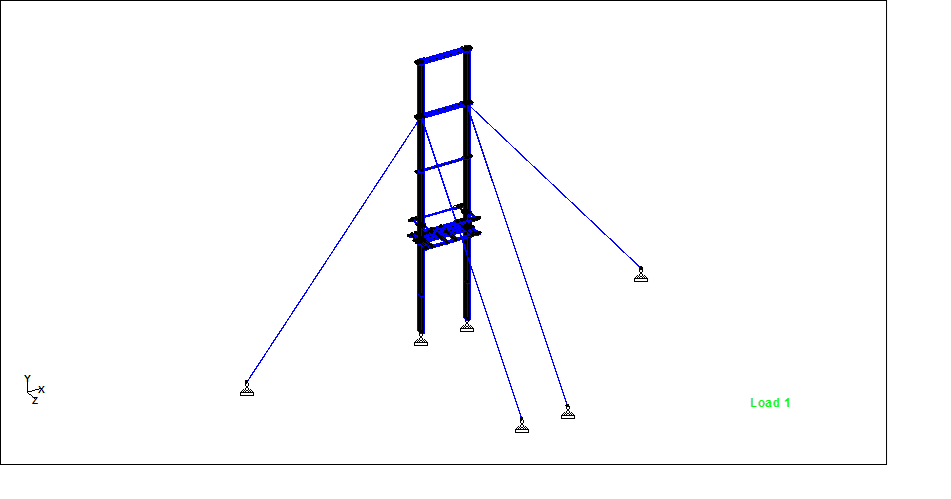
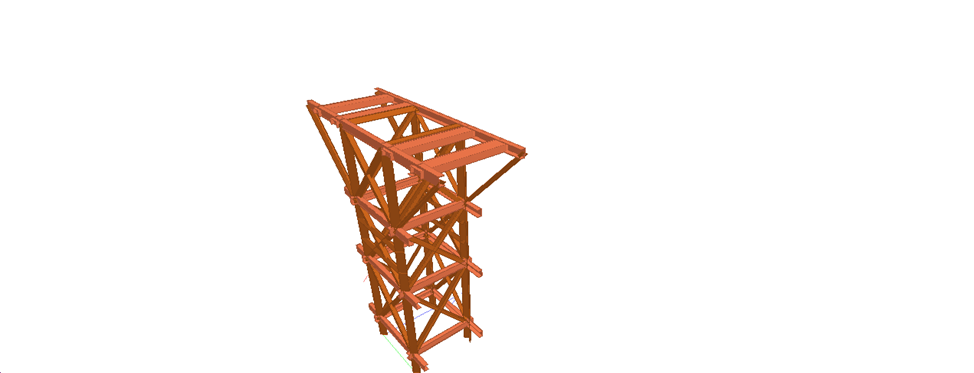
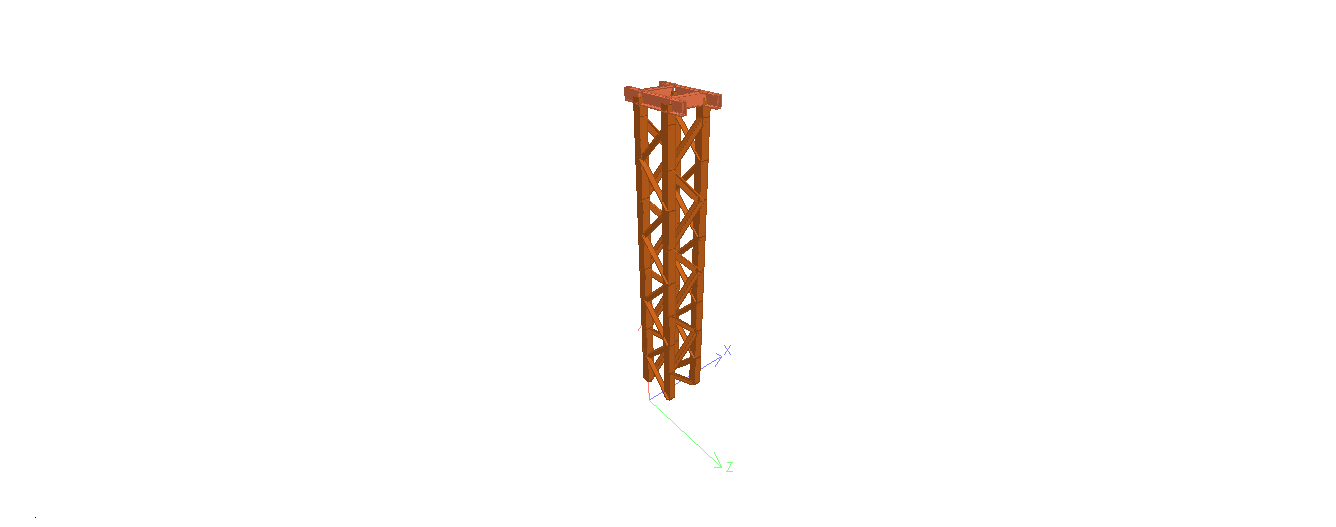
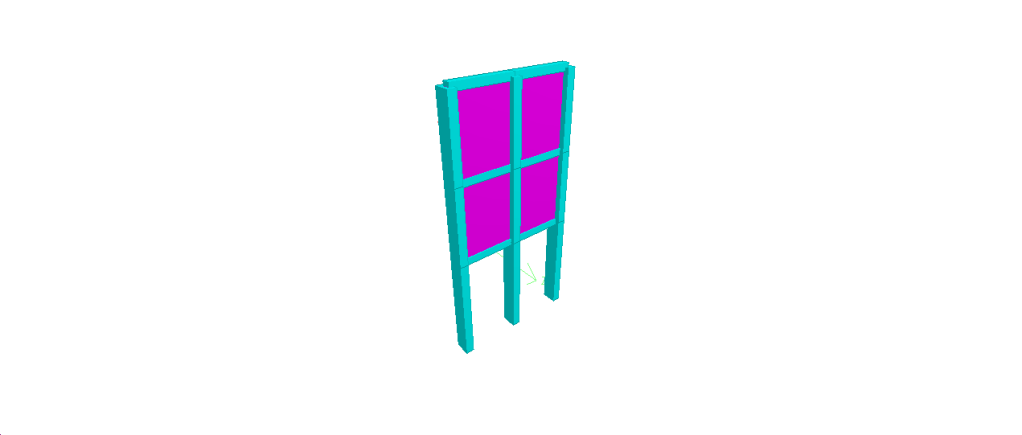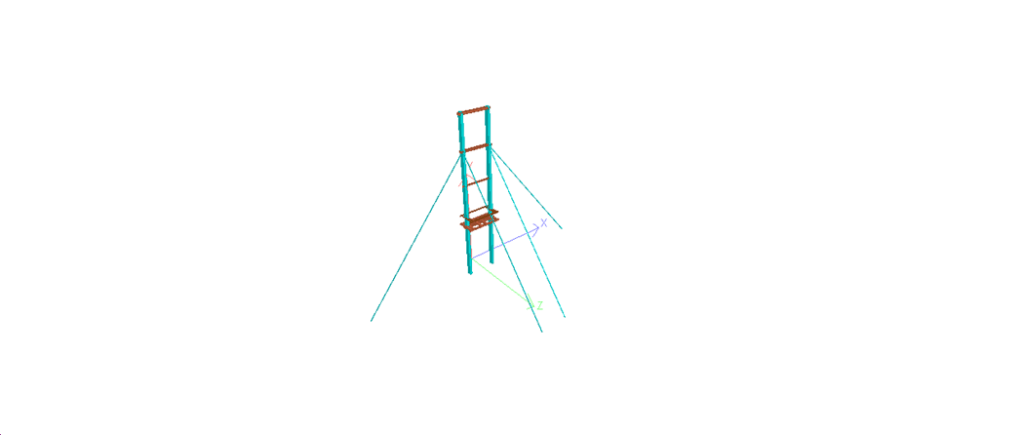Hello friends, Welcome to Design and Think World .Today, I am discussing Cable Post Supporting Structure Design.
- Purpose: – It is mainly used in 11/33 kV Distribution project as an overhead supporting arrangement for Cable.
- Location Selection: –To be determined by the density of existing services, likely disruption to traffic and space requirements for construction of cable post.
- Dimension: – Height =Normally 4.5 to 5 meter from FGL (assume ) ,Top Platform Size = 1meter *1 meter (assume)
- STAAD MODEL :- STEEL/CONCRETE both
- CODAL PROVISION: – Structural steel shall be designed in accordance with the ‘General Construction in steel Code of Practice (IS 800 LSD) & Concrete shall be designed in Concrete code of practice (IS 456:2000).